Troubleshoot pipelines with Maia🔗
Maia provides intelligent pipeline monitoring and troubleshooting capabilities that help you identify and resolve issues quickly. This guide covers how to use Maia for anomaly detection, root cause analysis, and guided pipeline recovery.
Accessing pipeline runs🔗
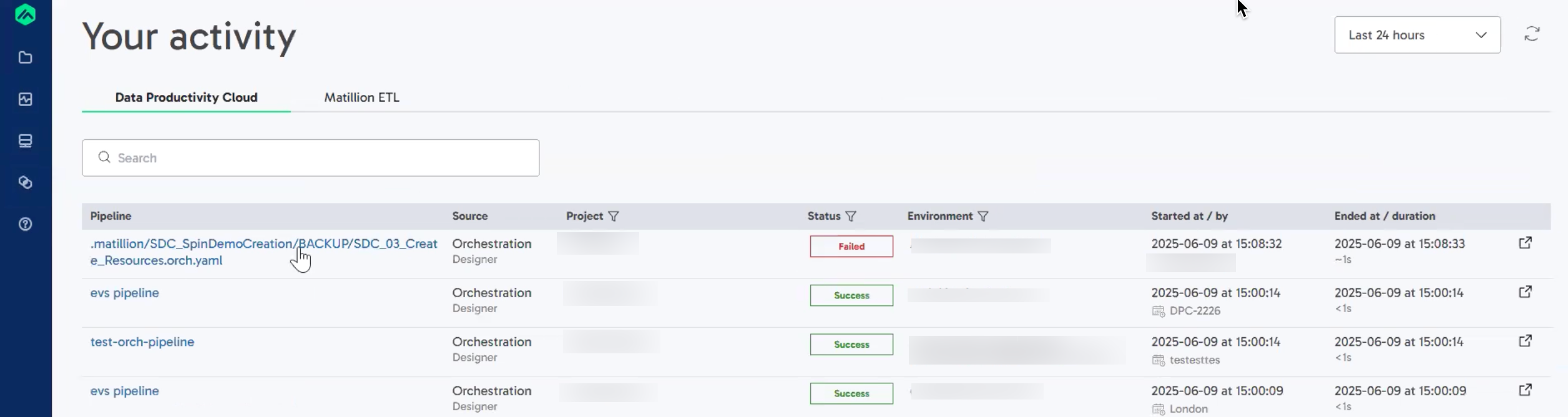
To view your pipeline execution history, click the Activity icon ![]() , then Pipeline Runs. Here, you can view a list of recent pipeline executions, along with their status (Success or Failed), and any anomaly indicators.
, then Pipeline Runs. Here, you can view a list of recent pipeline executions, along with their status (Success or Failed), and any anomaly indicators.
Fix with Maia🔗
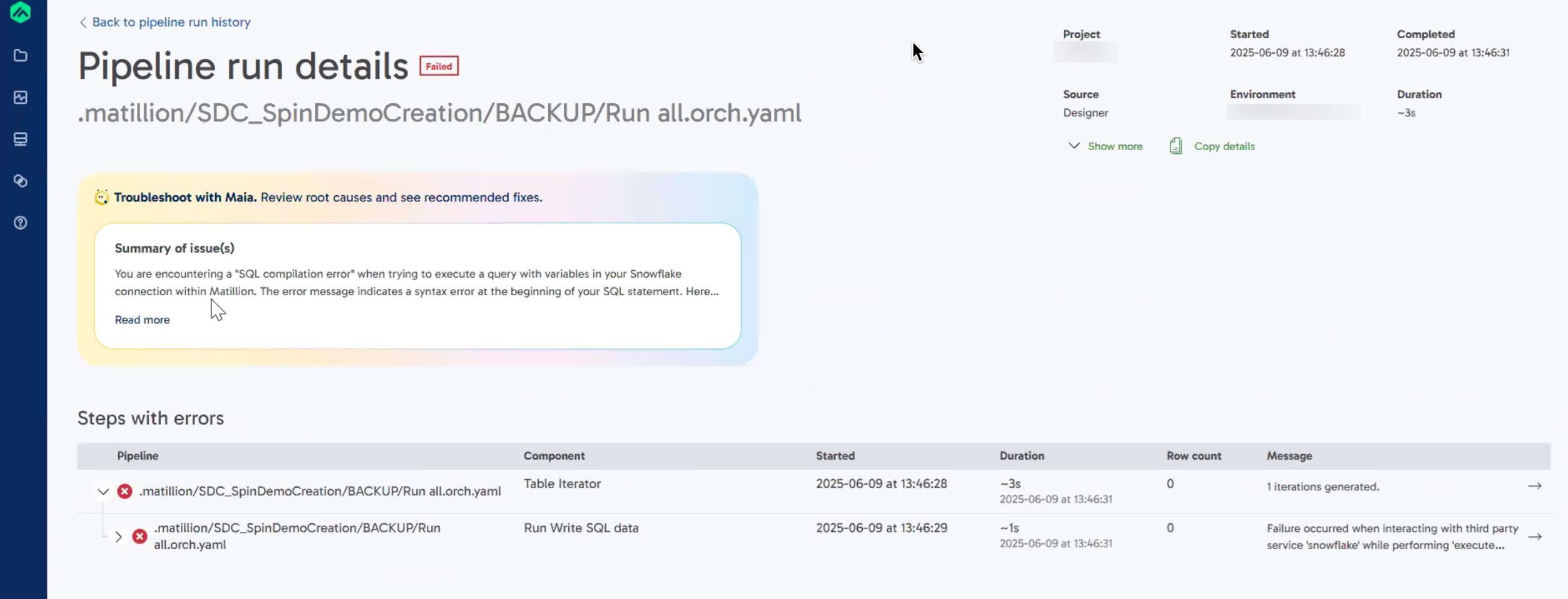
When a scheduled or API executed pipeline fails and the observability system generates a Root Cause Analysis (RCA), a Fix with Maia button appears in the Troubleshoot with Maia banner at the top of the Pipeline run details page. Click this button to start a guided recovery process. Maia will help you apply the recommended fixes identified during the RCA.
Follow these steps to recover your pipeline with Maia:
- Click Fix with Maia to open the dialog.
- Enter the following details to create a new branch for applying fixes to your pipeline:
- Branch Name: Provide a unique name for the new working branch where the fixes will be applied.
- Base Branch: Select the source branch from which the new branch will be created. Our recommendation is to branch from the
mainbranch. - Environment: Choose the environment where the new branch will be deployed.
- Click Get started to proceed.
You will be redirected to the Designer canvas in the newly created branch, where Maia will instantly begin working in the background to apply the necessary changes to resolve the fault. After Maia applies the fixes:
- Compare the changes Maia has made against the original code.
- Complete the fix by committing the changes, pushing the local changes to the remote repository, and publishing your pipeline. For more information about using source control, read Git in Designer.
Anomaly detection🔗
Maia automatically monitors your scheduled pipeline runs and flags significant deviations from expected behavior. This helps you detect potential issues before they become failures.
Maia uses statistical modeling to compare each scheduled pipeline run against historical trends. When execution time falls significantly outside the expected range, Maia flags the run as an anomaly. Anomaly detection currently provides visual indicators only—no alerts are triggered (such as email notifications).
Note
Maia requires at least 10 prior scheduled runs of the same pipeline to establish a reliable trend for anomaly detection.
Anomaly indicators🔗
In the Pipeline Runs dashboard, anomalies are displayed with:
- Red arrows (up/down) highlighting anomalies next to duration metrics
- Tooltips with details when you hover over the indicator (for example: "7.8% longer than expected based on recent runs")
- Anomalies section listing all detected anomalies for the run
Common anomaly scenarios🔗
| Scenario | Example | Anomaly type |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure performance | Load times spike due to backend slowness | Execution time higher |
| Optimization or refactoring | Code change makes execution faster than usual | Execution time lower |
| Source data changes | Upstream table has significantly more data | Execution time higher |
| Schema or configuration updates | Business logic change affects processing | Execution time varies |
Root cause analysis🔗
When a pipeline fails, Maia automatically analyzes the error and provides context-aware diagnostics to help you understand what went wrong.
To analyze the root cause of a failure:
- In Pipeline Runs, click on any pipeline with a Failed status.
- On the Pipeline run details page, you'll see the Troubleshoot with Maia banner at the top.
Maia automatically:
- Identifies the exact location where the error occurred
- Summarizes the issue in plain language
- Suggests recommended fixes
Example: SQL compilation error🔗
In this example, a SQL compilation error was caused by incorrect variable usage in a Snowflake query. Maia identified the exact line where the syntax error occurred, highlighted the type of issue, and suggested an appropriate fix.