Reverting from external to internal security🔗
Overview
This document describes how to revert to an internal security configuration following accidental misconfiguration of external security in a Matillion ETL instance. Configuring internal and external security can be done by clicking Admin and then clicking User Configuration.
There are three types of security options available for user configuration.
- None
- Internal
- External
When selecting External, the Matillion ETL instance will link to an existing directory server. For example: OpenLDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) or Microsoft Active Directory.
Please Note
Opting to use External security will prevent existing users configured in Internal security from logging in.

External security misconfiguration can result in being locked out of Matillion, with no way to regain access other than by editing the configuration files on the Matillion server.
Matillion users can revert to an internal security configuration by editing the following files and confirming the information is correct.
/usr/share/emerald/WEB-INF/classes/Emerald.properties/usr/share/emerald/WEB-INF/security.fragment/etc/tomcat/server.xml(Snowflake and Amazon Redshift)/etc/tomcat/server.xml(Google BigQuery)/etc/tomcat/tomcat-users.xml(Snowflake and Amazon Redshift)/etc/tomcat/tomcat-users.xml(Google BigQuery)
Important Information
This guide uses examples using a Tomcat version of the server.
Please follow the steps mentioned below to revert to an internal security configuration.
Move sudo to root
To begin the restore, SSH into the Matillion instance and sudo to root:
sudo -i

Stop Matillion ETL
First, stop the Matillion ETL service:
Snowflake and Amazon Redshift:
service tomcat stop
Google BigQuery:
service tomcat stop

Emerald.properties
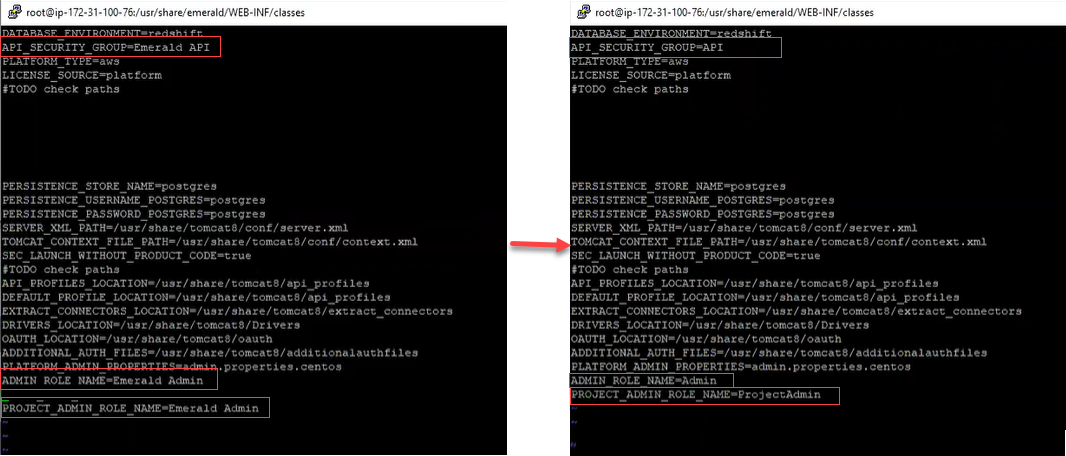
The file /usr/share/emerald/WEB-INF/classes/Emerald.properties is Matillion-specific and contains a number of authorization parameters.
The file format is UTF-8 text, containing lines with KEY=value pairs.
The following parameters must be present:
API_SECURITY_GROUP=APIADMIN_ROLE_NAME=AdminPROJECT_ADMIN_ROLE_NAME=ProjectAdmin
Please ensure that your parameters are the same as above.
security.fragment
The file /usr/share/emerald/WEB-INF/security.fragment is used by Tomcat to control access to parts of the Matillion ETL application.
The format is XML.
Please ensure that the security.fragment file you use matches the file provided:
Click here to download this security.fragment file.
server.xml
The file /etc/tomcat/server.xml (Snowflake and Amazon Redshift) or /etc/tomcat/server.xml (Google BigQuery) is the main Tomcat configuration file. Security is controlled by means of a Realm, and this needs to be replaced.
Look for the <Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.JNDIRealm" …> element and DELETE it.
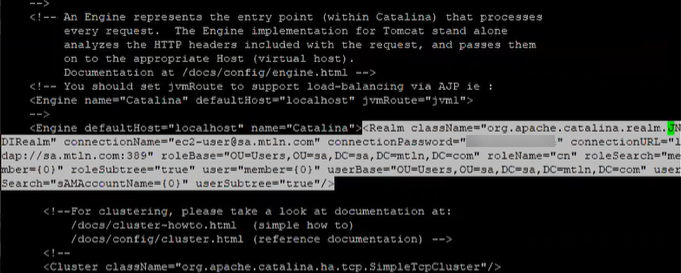
Next, in the file server.xml and inside the <Engine defaultHost="localhost" name="Catalina"> add a new Realm referencing the user database:
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.LockOutRealm"> <Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.UserDatabaseRealm"><CredentialHandler algorithm="SHA-512" className="org.apache.catalina.realm.MessageDigestCredentialHandler"/></Realm></Realm>

tomcat-users.xml
(Snowflake and Amazon Redshift) The file /etc/tomcat/tomcat-users.xml is the "user database" referred to in the above server.xml Realm.
(Google BigQuery) The file /etc/tomcat/tomcat-users.xml is the "user database" referred to in the above server.xml Realm.
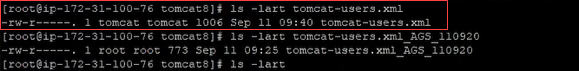
Ensure that the file has permission mode 644, and is owned by the tomcat : tomcat.
Please Note
The commands you can use to get the information are as follows:
chmod 644 tomcat-users.xmlchown tomcat:tomcat tomcat.users.xml
Setting your password
To set up the password, you need to go to cat tomcat-users.xml. The content should be as follows:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <tomcat-users xmlns="http://tomcat.apache.org/xml" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://tomcat.apache.org/xml tomcat-users.xsd" version="1.0"> <role rolename="Emerald"/> <role rolename="API"/> <role rolename="Admin"/> <user username="ec2-user" password="YourPassword" roles="Emerald,ProjectAdmin,API,Admin"/> </tomcat-users>

Encrypting your password
You will need to use the sha512 message digest function to generate the hash of your chosen password. For example, if you choose "change me" as the password, you can generate or encrypt the hash value using the following command:
echo -n "change me" | sha512sum | awk '{print $1}'
Then your entry in tomcat-users.xml would look like this:
<user username="ec2-user" password="94fd04a6099e3e42ee047bad6da61258afd7bc0637af5eae85441345e68cf0a53e839ba17a50ef85c79d9996a3cb555c0c612cd3a0dd6fe7a77ece820480d496" roles="Emerald,API,Admin"/>

You will use the username and password to connect to the Matillion ETL web user interface once the service has been restarted.
Service restart
There are occasional problems with file and directory permissions caused by YUM updates. Matillion offers a shell script to correct them.
Before restarting the service, please run:
/usr/share/emerald/WEB-INF/classes/scripts/matillion_ensure.sh

Now that the configuration files have been repaired, you can restart the Matillion service:
Snowflake and Amazon Redshift:
service tomcat start
Google BigQuery:
service tomcat start

Monitor the startup progress with the following command:
Snowflake and Amazon Redshift:
tail -f /var/log/tomcat/catalina.out
Google BigQuery:
tail -f /var/log/tomcat/catalina.out

After anywhere between 20 seconds and 2 minutes, you should find a message like this:
org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina.start Server startup in ? ms
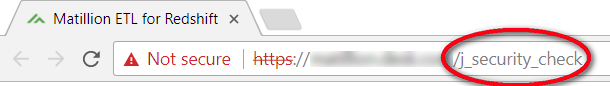
You are now ready to reconnect to the Matillion web user interface. Ensure there is no j_security_check suffix in the URL:
You should now be able to log in successfully with your credentials from tomcat-users.xml.
