Using data structure variables🔗
Overview
The data structure variable type lets users dynamically populate parameters that require a structured object. Users can then parameterize and automate their jobs that extract and flatten nested data.
The data structure variable accepts serialized JSON as a value, which describes the structure of the data to use as input in compatible components.
The following components use the data structure scalar variable:
- Extract components, such as API Extract (Snowflake, Redshift, BigQuery).
- Extract Nested Data (Snowflake, Redshift, BigQuery, Delta Lake on Databricks).
- Nested Data Load (Redshift).
Creating a data structure environment variable
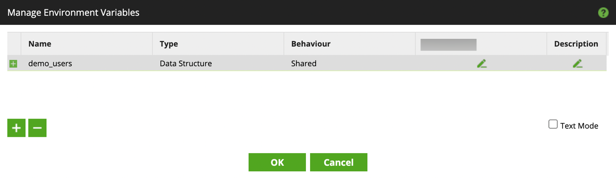
1. Click Project → Manage Environment Variables.
Alternatively, click the Export component tab. Then click Manage Variables → Manage Environment Variables.
2. Click to add a new environment variable.
If the variable name does not meet the intrinsic requirements, the following error message will be displayed:
The name [variable-name] must start with a letter, underscore or $ symbol followed by any number of alphanumerics, underscores and $ symbols.
3. In the Type column, select Data Structure.
4. In the column named after the current environment, click the edit button (pencil icon) to open Create Data Structure Variable.
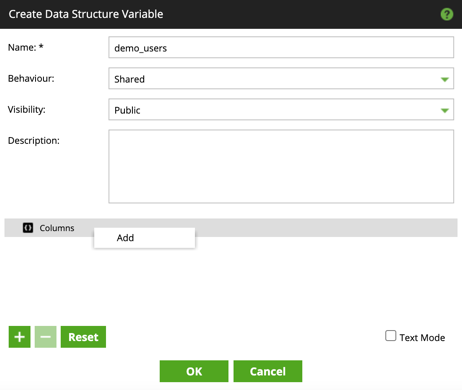
5. The Create Data Structure Variable dialog allows fine-grained metadata setup. Right-click Columns and click Add to open the Add Column dialog. Alternatively, check the Text Mode checkbox to open the text editor.
Properties and their descriptions for Add Column are listed below.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Column Name | A field for the new column. |
| Column Type | Select from Field, Array, or Struct. |
| Data Type | A data type for the new column. Only selectable if the Column Type is Field. |
| Size | Set the column size. Only selectable if the Data Type is Text. |
| Precision | Set the column precision. Only selectable if the Data Type is Numeric. |
| Scale | Set the column scale. Only selectable if the Data Type is Numeric. |
6. Click OK to confirm the setup.
Exporting data to the data structure variable
Data from a data source can be exported to a data structure variable, autopopulating the variable's data structure as opposed to doing this manually in the steps above.
1. Click the Export component tab.
2. Click Edit to open the Export Variables dialog.
3. Click to add a new export.
4. In the Source dropdown, select Data Structure.
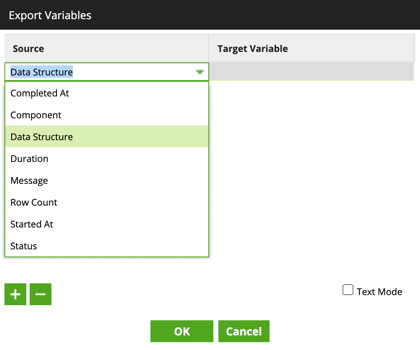
5. In the Target Variable dropdown, select the name of the data structure to be populated.
Using data structure variables in a job
Below is an orchestration job with an API Extract component and a Python Script component. The API Extract component is using a custom Extract Profile from an endpoint that provides dummy data. Read Manage Extract Profiles to learn more about creating an Extract Profile.
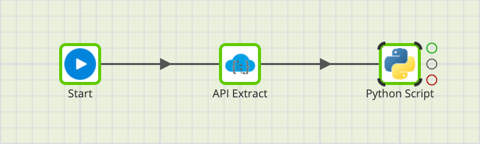
The data source, called Users, has been exported to a data structure variable. The Python Script component is used to output the variable at runtime using the command: print(variable-name).
The output is viewable in the Tasks tab after the job has run.
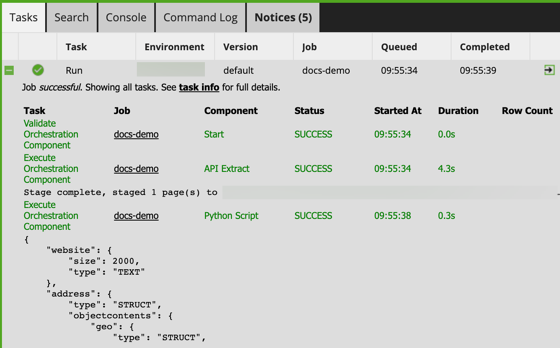
Using a transformation job, the nested data can be flattened using an Extract Nested Data component with the Table Input component.